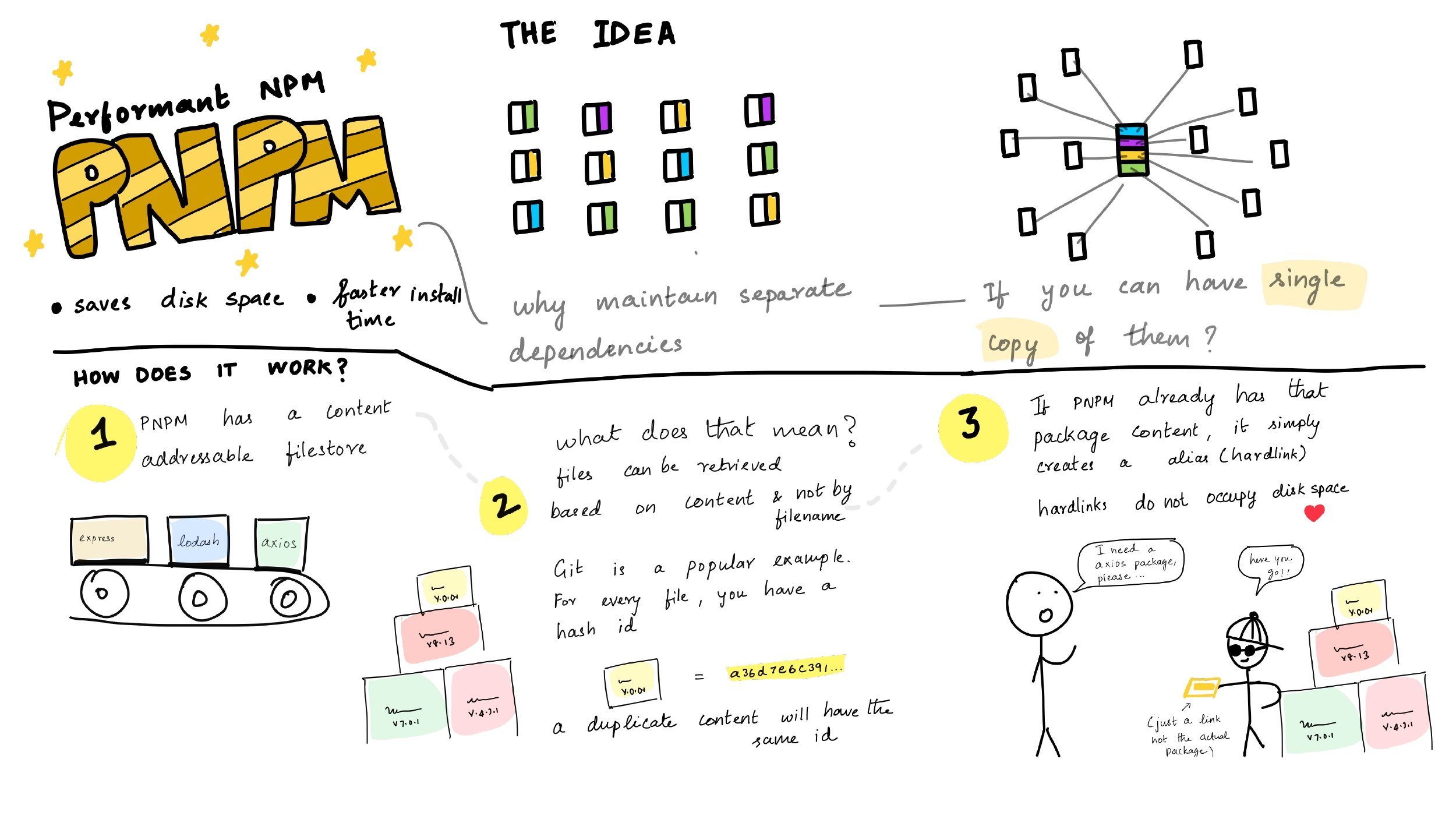
vue-cli-service 机制 npm run dev 之后发生了些什么???
入口 从package.json里面可以看到npm run dev其实就是vue-cli-service serve
vue-cli3.0 安装的时候把vue-cli-service一并安装了,即执行了npm install vue-cli-service --save-dev
这样就可以在./node_modules/.bin目录下查看到vue-cli-service
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @IF EXIST "%~dp0\node.exe" ( "%~dp0\node.exe" "%~dp0\..\@vue\cli-service\bin\vue-cli-service.js" %* ) ELSE ( @SETLOCAL @SET PATHEXT=%PATHEXT:;.JS;=;% node "%~dp0\..\@vue\cli-service\bin\vue-cli-service.js" %* )
入口:./node_modules/@vue/cli-service/bin/vue-cli-service.js
瞅一眼vue-cli-service.js的核心代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 const Service = require ('../lib/Service' )const service = new Service(process.env.VUE_CLI_CONTEXT || process.cwd())const rawArgv = process.argv.slice(2 )const args = require ('minimist' )(rawArgv, { boolean: [ 'modern' , 'report' , 'report-json' , 'watch' , 'open' , 'copy' , 'https' , 'verbose' ] }) const command = args._[0 ]service.run(command, args, rawArgv).catch(err => error(err) process.exit(1 ) })
初始化配置 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 module .exports = class Service constructor (context, { plugins, pkg, inlineOptions, useBuiltIn } = {}) { process.VUE_CLI_SERVICE = this this .initialized = false this .context = context this .inlineOptions = inlineOptions this .webpackChainFns = [] this .webpackRawConfigFns = [] this .devServerConfigFns = [] this .commands = {} this .pkgContext = context this .pkg = this .resolvePkg(pkg) this .plugins = this .resolvePlugins(plugins, useBuiltIn) this .modes = this .plugins.reduce((modes, { apply: { defaultModes }} ) => { return Object .assign(modes, defaultModes) }, {}) } }
获取package.json中的依赖。通过read-pkg这个包读取package.json文件,并以JSON格式返回赋值给this.pkg。
初始化相关插件。相关插件包括:内联插件、package.json中的cli-plugin-*插件。内联插件包含serve、build、inspect等。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 resolvePlugins (inlinePlugins, useBuiltIn) { const idToPlugin = id => id: id.replace(/^.\// , 'built-in:' ), apply: require (id) }) let plugins const builtInPlugins = [ './commands/serve' , './commands/build' , './commands/inspect' , './commands/help' , './config/base' , './config/css' , './config/dev' , './config/prod' , './config/app' ].map(idToPlugin) if (inlinePlugins) { } else { const projectPlugins = Object .keys(this .pkg.devDependencies || {}) .concat(Object .keys(this .pkg.dependencies || {})) .filter(isPlugin) .map(idToPlugin) plugins = builtInPlugins.concat(projectPlugins) } }
初始化模式。解析每个命令使用的默认模式,例如serve对应的development,build对应production。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 this .modes = this .plugins.reduce((modes, { apply: { defaultModes }} ) => { return Object .assign(modes, defaultModes) }, {})
内联插件默认导出了一个defaultModes
1 2 3 4 module .exports.defaultModes = { serve: 'development' }
为什么要初始化模式?
解析命令行参数 minimist解析工具来对命令行参数进行解析。shell命令携带的参数解析出来。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 const args = require ('minimist' )(rawArgv, { boolean: [ 'open' , 'copy' , 'https' , ] })
加载插件 运行service.run方法,加载环境变量,加载用户配置,应用插件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 async run (name, args = {}, rawArgv = []) { const mode = args.mode || (name === 'build' && args.watch ? 'development' : this .modes[name]) this .init(mode) args._ = args._ || [] let command = this .commands[name] const { fn } = command return fn(args, rawArgv) }
加载环境变量,从项目根目录下的.env.(mode)文件读取环境变量,并写入到process.env(声明环境变量必须是VUE_APP_*,不然会被过滤掉)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 init (mode = process.env.VUE_CLI_MODE) { if (mode) { this .loadEnv(mode) } this .loadEnv() } loadEnv (mode) { const basePath = path.resolve(this .context, `.env${mode ? `.${mode} ` : `` } ` ) const localPath = `${basePath} .local` const load = path => const env = dotenv.config({ path, debug : process.env.DEBUG }) dotenvExpand(env) logger(path, env) } load(localPath) load(basePath) if (mode) { const defaultNodeEnv = (mode === 'production' || mode === 'test' ) ? mode : 'development' if (shouldForceDefaultEnv || process.env.NODE_ENV == null ) { process.env.NODE_ENV = defaultNodeEnv } } }
加载用户配置。读取vue.config.js文件内部的配置
1 2 3 4 5 init (mode = process.env.VUE_CLI_MODE) { const userOptions = this .loadUserOptions() this .projectOptions = defaultsDeep(userOptions, defaults()) }
应用插件。前面初始化插件的时候(resolvePlugins方法)有一个apply属性,调用这个方法就可以导入对应的插件,这里就是调用了serve.js的方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 init (mode = process.env.VUE_CLI_MODE) { this .plugins.forEach(({ id, apply } ) => { apply(new PluginAPI(id, this ), this .projectOptions) }) if (this .projectOptions.chainWebpack) { this .webpackChainFns.push(this .projectOptions.chainWebpack) } if (this .projectOptions.configureWebpack) { this .webpackRawConfigFns.push(this .projectOptions.configureWebpack) } } }
注册命令。在service注册serve命令(前面run方法最后调用了fn函数,也就是registerCommand的第三个参数)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 api.registerCommand('serve' , { description: 'start development server' , usage: 'vue-cli-service serve [options] [entry]' , options: {} }, async function serve (args ) });
配置、启动服务 最终执行的serve.js 内注册serve时传递的方法。webpack获取到配置之后,实例化Compiler 传递给webpackDevServer,通过webpackDevServer实现自动编译和热更新。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 async function serve (args ) const compiler = webpack(webpackConfig) const server = new WebpackDevServer(compiler, Object .assign({ clientLogLevel: 'none' , historyApiFallback: { disableDotRule: true , rewrites: [ { from : /./ , to: path.posix.join(options.baseUrl, 'index.html' ) } ] }, contentBase: api.resolve('public' ), watchContentBase: !isProduction, hot: !isProduction, quiet: true , compress: isProduction, publicPath: options.baseUrl, overlay: isProduction ? false : { warnings : false , errors : true } }, projectDevServerOptions, { https: useHttps, proxy: proxySettings, })) return new Promise ((resolve, reject ) => { compiler.hooks.done.tap('vue-cli-service serve' , stats => }) server.listen(port, host, err => if (err) { reject(err) } }) }) }
获取 webpack 配置:api.resolveWebpackConfig()
获取 devServer 配置
注入 webpack-dev-server 和 hot-reload(HRM)中间件入口
创建 webpack-dev-server 实例
启动webpack-dev-server后,在目标文件夹中是看不到编译后的文件的,实时编译后的文件都保存到了内存当中。